3D printing (also called “additive manufacturing”) allows businesses to fabricate a variety of goods in small quantities over a short period of time, ranging in use from automotive and aerospace to manufacturing (and even collectables).
Recently, the Seiko Epson Corporation (Epson) announced that it has developed an industrial 3D printer that can use common third-party materials to “produce strong, accurate industrial parts of various sizes and functions.” The clear goal is to make the device as wide-reaching as possible since it can utilize different materials to produce parts for final products. The design also helps to reduce costs for Epson as they don’t have to create and maintain their own printable materials and can rely on other companies to supply their device.
 |
| Source: Epson |
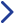
Standard industrial 3D printers require the use of special modeling materials (e.g., resins, soft metals, foodstuffs). This means that many of the products are not well-suited for pieces requiring a lot of tensile strength, so their use in industrial parts for final products has been limited. Epson's newly developed 3D printer employs a unique material extrusion method that is achieved using a flat screw (an inline screw with a flattened configuration) like that found in Epson's precision injection molding machines. This extrusion method enables the printer to be used with several third-party materials, such as resin or metal pellets that are generally available at lower cost than other materials, environmentally considerate biomass pellets, and PEEK materials (which can provide high heat resistance).
| Model of Flat Screw |
 |
| Source: Epson |
The amount of material injected is controlled by regulating the pressure within the head as well as monitoring the action of a valve that works in concert with the modeling speed. The temperature at the surface of a piece being printed must also be controlled to maintain the required strength of the final product. Epson employs a unique mechanism to precisely control this temperature and to achieve the proper strength and accuracy—making this 3D printer a device designed to manufacture strong, accurate objects with commonly available materials. It is also suited to mass customization as it can produce small batches of parts tailored to customers' needs with enhanced quality, short lead times, and at a fraction of the cost of traditional manufacturing processes.
Epson is hoping to commercialize the printer after first making needed refinements while utilizing it internally to volume-produce certain parts for commercial and industrial equipment. The company will be showing the device at their booth at the International Robot Exhibition 2022, which opens on March 9th at the Tokyo International Exhibition Center (also called “Tokyo Big Sight”).
Keypoint Intelligence Opinion
Epson’s latest fore into additive manufacturing could be big boon for the company. Beyond pursuing a market growing in interest, the company believes that this device can “innovate manufacturing by co-creating flexible, high-throughput production systems that reduce environmental impact.” While this is a noble path to pursue, it’s also a great selling point for clients that want to be more conscious about their environmental footprint.
Log in to the InfoCenter to view research on additive manufacturing through our Functional & Industrial Printing Advisory Service. If you’re not a subscriber, just send us an email at sales@keypointintelligence.com for more info.